Advanced Chunking for RAG Improvement
1. Introduction
Chunking is the process of dividing long text into smaller fragments called chunks. In RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pipelines, this process is an important stage because chunks are used to create vector embeddings and semantic information search. We search for the closest pieces (chunks) for the user's query and pass them to the LLM to generate answers to queries. The better a document is split into text chunks, the higher the probability that the model will be able to find and provide accurate and relevant information.
What's the complexity? Financial documents, such as company PDF reports, contain complex structure: headings, tables, lists, and text blocks, with complex layout and block placement. If documents are processed and split into chunks incorrectly, this will negatively affect answer quality.
The goal of this guide is to demonstrate how results differ when we use basic chunking from langchain and more advanced CompressaChunking, which takes document structure into account and, for example, recognizes tables.
Our guide will include the following steps:
- Loading a financial PDF presentation and chunking with langchain
- Repeating the basic langchain RAG pipeline from the guide "Basic RAG in 15 Minutes"
- Testing the pipeline on test questions
- Improving chunking process quality
- Re-testing and evaluating results
2. Environment Setup
Let's install and import the necessary libraries:
#!pip install langchain
#!pip install langchain-openai
#!pip install langchain_community
#!pip install requests
#!pip install beautifulsoup4
#!pip install gdown
#!pip install faiss-cpu - if you're running on CPU
#!pip install faiss-gpu - if you're running on GPU with CUDA support
import os
import requests
import gdown
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings, ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
os.environ["COMPRESSA_API_KEY"] = "your_key"
# If you're running locally on Macbook, also set the following environment variables
# os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false"
# os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
3. Document Processing and Chunking Using Langchain
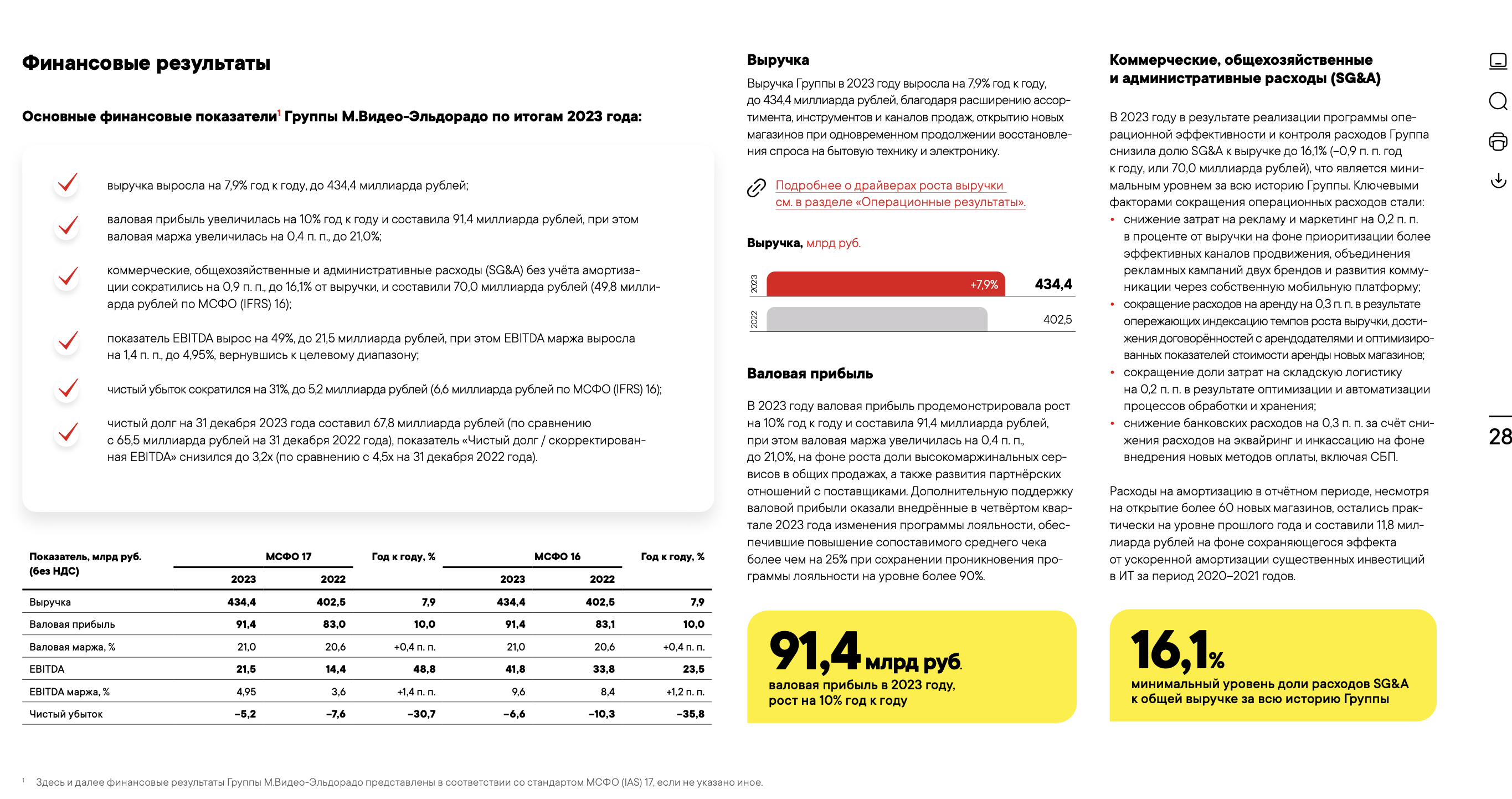
We'll work with an annual PDF presentation report, publicly available on the Mvideo-Eldorado company website. To speed up processing for this guide, I've limited the presentation to 6 slides. Example of one of the slides:
First, let's load the PDF file and apply basic chunking algorithm using langchain's standard tool — RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.
This tool simply splits text by a given number of characters, without taking document structure into account.
# Download the required PDF file from Compressa's Google Drive
file_id = '14sA1-B90nwwTZr3A9V1J0NfNpTYYguMy'
url = f'https://drive.google.com/uc?id={file_id}'
gdown.download(url, 'mvideo_report.pdf', quiet=False)
loader = PyPDFLoader("mvideo_report.pdf")
# Load PDF pages as Langchain documents
documents = loader.load()
# Configure chunking parameters
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000, # Size of each chunk
chunk_overlap=20, # Adding adjacent characters to chunk
add_start_index=True
)
# Split PDF document into chunks
chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
# Check the number of chunks (should be 20)
print(f"Total chunks created: {len(chunks)}")
# Let's look carefully at the obtained chunks.
# Notice how such a "primitive" document chunking strategy breaks thoughts between chunks.
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Chunk {i+1}:\n{chunk.page_content}\n")
4. Repeating Basic Langchain RAG Pipeline
Let's repeat the basic RAG pipeline based on langchain that we already covered in the guide "Basic RAG in 15 Minutes". We'll just copy it and won't go through it again.
Important Change!
To demonstrate improvements from a more advanced chunking strategy, we'll search and pass to the LLM only 1, the most relevant piece of the document.
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(api_key=os.getenv("COMPRESSA_API_KEY"), base_url="https://compressa-api.mil-team.ru/v1", model="Compressa-Embeddings")
# Create and populate vector store
vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(chunks, embeddings)
print("Vector store successfully created")
# Create mechanism for searching needed chunks, search for 1 most relevant
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 1})
# Configure LLM for generating answers
llm = ChatOpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("COMPRESSA_API_KEY"), base_url="https://compressa-api.mil-team.ru/v1", model="Compressa-LLM")
system_template = f"""You are an intelligent assistant in Russian that answers user questions based on provided information. Use the following contextual information,
to answer the question. If there's no answer in the context, answer 'I don't know the answer to the question'.
Answer as accurately as possible, but briefly if possible."""
qa_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system_template),
("human", """Contextual information:
{context}
Question: {input}
"""),
])
# Create chain for answering questions
document_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, qa_prompt)
rag_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, document_chain)
def ask_question(question):
response = rag_chain.invoke({"input": question})
return response["answer"]
4. Testing on Test Questions
Let's see if our RAG assistant can answer several questions about the document:
questions = [
"What happened in May?",
"When did Casarte brand sales start?",
"What does the company plan to focus on in warranty and post-warranty service?",
"By how much % did EBITDA increase year-over-year according to IFRS 17?",
]
print("\nUsing RAG pipeline:")
for question in questions:
print(f"\nQuestion: {question}")
print(f"RAG Answer: {ask_question(question)}")
Let's compare the obtained results with correct answers:
Question: What happened in May?
Correct answer: The Group became the largest operator of electronic waste in Russia and a key partner of the first electronics recycling plant complex in Russia "Ecopolis Corporation".
Question: When did Casarte brand sales start?
Correct answer: In December
Question: What does the company plan to focus on in warranty and post-warranty service?
Correct answer: The Group plans to additionally focus on providing a wide range of specialized tools – extended warranty, product insurance
Question: By how much % did EBITDA increase year-over-year according to IFRS 17?
Correct answer: 48.8%
Most likely, all 4 answers will be incorrect5. Improving Chunk Creation Process
To use more advanced document chunking strategies, let's send a request to the CompressaLayout API. We'll use the same chunk size (1000 characters) and specify additional settings available in this API. The full list of parameters can be viewed in the documentation.
# Specify URL and authorization headers
url = "https://compressa-api.mil-team.ru/v1/layout"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {os.environ['COMPRESSA_API_KEY']}",
"accept": "application/json",
}
# Specify our PDF file
files = {"files": open("mvideo_report.pdf", "rb")}
# Keep 2 settings from langchain tool and specify the rest
data = {
"xml_keep_tags": "false",
"output_format": "application/json", # Response format: JSON
"coordinates": "false", # We don't need element coordinates
"strategy": "fast", # Use fast document processing strategy, since text can be copied from file
"chunking_strategy": "by_title", # Use headings for chunking
"combine_under_n_chars": 800, # Combine if less than 800 characters
"max_characters": 1000, # Maximum 1000 characters per chunk
"multipage_sections": "false", # Don't allow chunks to span multiple pages
"overlap": 20, # Adding adjacent characters to chunk
"starting_page_number": 1, # Start from first page
"languages": ["rus", "eng"] # Languages used in the document
}
# Execute API request
response = requests.post(
url,
headers=headers,
files=files,
data=data
)
# Save results and check obtained chunks
result = response.json()
print(str(result)[:1000])
# Convert API response to format understandable for Langchain
chunks = []
for item in result:
# Create Document objects for each chunk
text = item['text'] # Extract text from JSON
chunk = Document(page_content=text)
chunks.append(chunk)
# Output all chunks after chunking
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Chunk {i+1}:\n{chunk.page_content}\n")
6. Re-testing and Evaluating Results
You can notice that chunks now better match the presentation structure. Let's populate the new vector store:
# Create and populate new vector store
vectorstore2 = FAISS.from_documents(chunks, embeddings)
print("Vector store successfully created")
# Create mechanism for searching needed chunks in new store
retriever2 = vectorstore2.as_retriever(search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 1})
rag_chain2 = create_retrieval_chain(retriever2, document_chain)
def ask_question2(question):
response = rag_chain2.invoke({"input": question})
return response["answer"]
print("\nUsing RAG pipeline:")
for question in questions:
print(f"\nQuestion: {question}")
print(f"RAG Answer: {ask_question2(question)}")
Let's compare the obtained results with correct answers:
Question: What happened in May?
Correct answer: The Group became the largest operator of electronic waste in Russia and a key partner of the first electronics recycling plant complex in Russia "Ecopolis Corporation".
Question: When did Casarte brand sales start?
Correct answer: In December
Question: What does the company plan to focus on in warranty and post-warranty service?
Correct answer: The Group plans to additionally focus on providing a wide range of specialized tools – extended warranty, product insurance
Question: By how much % did EBITDA increase year-over-year according to IFRS 17?
Correct answer: 48.8%
Notice that now all answers are correct. Thanks to proper document chunking, we didn't break context between individual pieces, so the LLM received correct, complete information and was able to give an accurate answer to the question.You can also improve search accuracy using the CompressaRerank model, which additionally prioritizes found passages for the user's query. We've prepared a special guide for this.
If you want to dive deeper into Embeddings and understand how semantic search works technically - check out another practical guide.